Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plot bootstrapped confidence interval for linear model fit¶
# Authors: Jose C. Garcia Alanis <alanis.jcg@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from mne.viz import plot_compare_evokeds
from mne.decoding import Vectorizer, get_coef
from mne.datasets import limo
from mne.evoked import EvokedArray
Here, we’ll import only one subject and use the data to bootstrap the beta coefficients derived from linear regression
# subject id
subjects = [2]
# create a dictionary containing participants data
limo_epochs = {str(subj): limo.load_data(subject=subj) for subj in subjects}
# interpolate missing channels
for subject in limo_epochs.values():
subject.interpolate_bads(reset_bads=True)
# epochs to use for analysis
epochs = limo_epochs['2']
# only keep eeg channels
epochs = epochs.pick_types(eeg=True)
# save epochs information (needed for creating a homologous
# epochs object containing linear regression result)
epochs_info = epochs.info
tmin = epochs.tmin
Out:
1052 matching events found
No baseline correction applied
Adding metadata with 2 columns
0 projection items activated
0 bad epochs dropped
Computing interpolation matrix from 117 sensor positions
Interpolating 11 sensors
use epochs metadata to create design matrix for linear regression analyses
# add intercept
design = epochs.metadata.copy().assign(intercept=1)
# effect code contrast for categorical variable (i.e., condition a vs. b)
design['face a - face b'] = np.where(design['face'] == 'A', 1, -1)
# create design matrix with named predictors
predictors = ['intercept', 'face a - face b', 'phase-coherence']
design = design[predictors]
extract the data that will be used in the analyses
# get epochs data
data = epochs.get_data()
# number of epochs in data set
n_epochs = data.shape[0]
# number of channels and number of time points in each epoch
# we'll use this information later to bring the results of the
# the linear regression algorithm into an eeg-like format
# (i.e., channels x times points)
n_channels = data.shape[1]
n_times = len(epochs.times)
# vectorize (channel) data for linear regression
Y = Vectorizer().fit_transform(data)
run bootstrap for regression coefficients
# set random state for replication
random_state = 42
random = np.random.RandomState(random_state)
# number of random samples
boot = 2000
# create empty array for saving the bootstrap samples
boot_betas = np.zeros((boot, Y.shape[1], len(predictors)))
# run bootstrap for regression coefficients
for i in range(boot):
# extract random epochs from data
resamples = random.choice(range(n_epochs), n_epochs, replace=True)
# set up model and fit model
model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False)
model.fit(X=design.iloc[resamples], y=Y[resamples, :])
# extract regression coefficients
boot_betas[i, :, :] = get_coef(model, 'coef_')
# delete the previously fitted model
del model
compute lower and upper boundaries of confidence interval based on distribution of bootstrap betas.
lower, upper = np.quantile(boot_betas, [.025, .975], axis=0)
fit linear regression model to original data and store the results in MNE’s evoked format for convenience
# set up linear model
linear_model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False)
# fit model
linear_model.fit(design, Y)
# extract the coefficients for linear model estimator
betas = get_coef(linear_model, 'coef_')
# project coefficients back to a channels x time points space.
lm_betas = dict()
ci = dict(lower_bound=dict(), upper_bound=dict())
# loop through predictors
for ind, predictor in enumerate(predictors):
# extract coefficients and CI for predictor in question
# and project back to channels x time points
beta = betas[:, ind].reshape((n_channels, n_times))
lower_bound = lower[:, ind].reshape((n_channels, n_times))
upper_bound = upper[:, ind].reshape((n_channels, n_times))
# create evoked object containing the back projected coefficients
# for each predictor
lm_betas[predictor] = EvokedArray(beta, epochs_info, tmin)
# dictionary containing upper and lower confidence boundaries
ci['lower_bound'][predictor] = lower_bound
ci['upper_bound'][predictor] = upper_bound
plot results of linear regression
# only show -250 to 500 ms
ts_args = dict(xlim=(-.25, 0.5))
# predictor to plot
predictor = 'phase-coherence'
# electrode to plot
pick = epochs.info['ch_names'].index('B8')
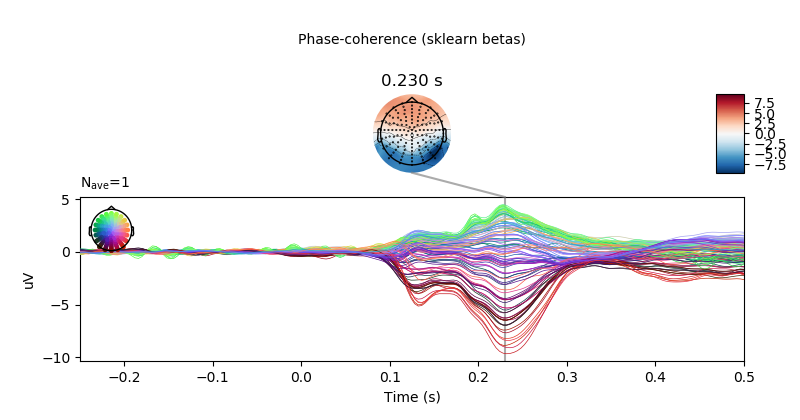
# visualise effect of phase-coherence for sklearn estimation method.
lm_betas[predictor].plot_joint(ts_args=ts_args,
title='Phase-coherence (sklearn betas)',
times=[.23])
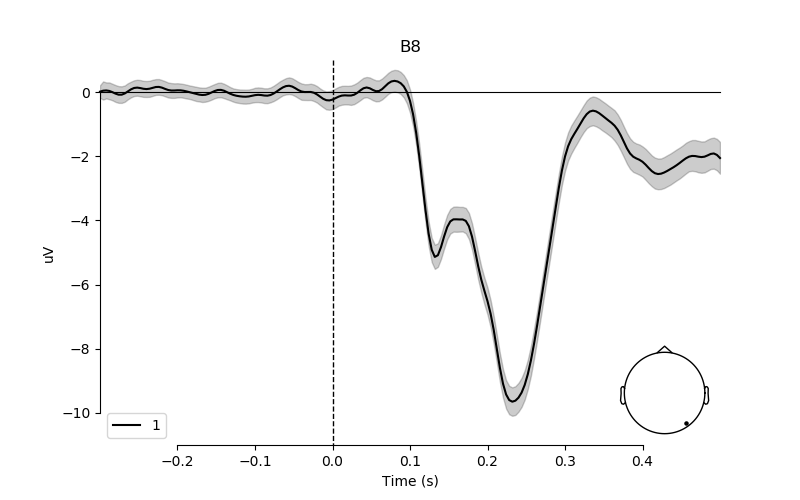
# create plot for the effect of phase-coherence on electrode B8
# with 95% confidence interval
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 5))
plot_compare_evokeds(lm_betas[predictor],
picks=pick,
ylim=dict(eeg=[-11, 1]),
colors=['k'],
legend='lower left',
axes=ax)
ax.fill_between(epochs.times,
ci['lower_bound'][predictor][pick]*1e6,
ci['upper_bound'][predictor][pick]*1e6,
color=['k'],
alpha=0.2)
plt.plot()
Total running time of the script: ( 19 minutes 49.079 seconds)